The Cell Chooses Which Metabolic Pathway to Use by
So Ill conform either M or end an M forms. All of the chemical reactions that take place inside of a cell are collectively called the cells metabolism.
4 1 Energy And Metabolism Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Metabolism is organised into distinct metabolic pathways to either maximise the capture of energy or minimise its use.

. The energy rich compound is formed. Because the different cells of the body can use fats and proteins for metabolism. A metabolic pathway is a series of chemical reactions that takes a starting molecule and modifies it step-by-step through a series of metabolic intermediates eventually yielding a final product.
So from here we can start kind of guessing our highest reaction rate if we raise the concentrations of S and cube. Energy state of the cell. Teo show the direction which a reaction moves and using red arrows with the minus sign to show where inhibition is occurring and using a reaction pathway they want us Tio describe what will happen in a certain situation.
Photosynthesis is performed in the chloroplast while respiration is in mitochonria. The respiration is a catabolic process. Cells are constantly carrying out thousands of chemical reactions needed to keep the cell and your body as a whole alive and healthy.
Mitochondria are organelles surrounded by two layers of membrane. A metabolic pathway is a series of steps found in biochemical reactions that help convert molecules or substrates such as sugar into different more readily usable materials. Metabolic function from a pathway-based perspective in addition to the traditional reaction- basedperspectiveThe algorithm and classicationschemedeveloped can be used to describe the pathway structure in annotated genomes to explore the capabilities of an organism.
A cells daily operations are accomplished through the biochemical reactions that take place within the cell. Several metabolic pathways are in specific locations inside of mitochondria. What are the 2 metabolic pathways a cell can use and what determines which pathway is used.
The metabolic pathway in the cell is regulated by covalent or non-covalent modifications. The matrix which is inside of both membranes is home to beta oxidation the citric acid cycle and some. B Control of metabolism is important in bioprocesses David R.
You can divide metabolic pathways into anabolic and catabolic categories. Its a good idea to draw out. Choose the true statement about metabolic pathways.
Polysaccharides are broken down into free sugars which are then metabolized as discussed in. Anabolic means that they require energy and use it to build large molecules from small ones. Search for the glycolysis pathway using the Pathway NameID option.
In eukaryotes the metabolic pathways occur within the cytosol and mitochondria of cells with the utilisation of glucose or fatty acids providing the majority of cellular energy in animals. Catabolic means that they release energy and break apart large molecules to make smaller ones. C Within a cell the flux.
These chemical reactions are often linked together in chains or pathways. B Metabolic pathways are sets of reactions that oxidize substrates. In the example of sugar metabolism the first metabolic pathway.
Tricarboxylic acid cycleTCA cycle or CREB cycle. Glucose CO 2 Anabolism Metabolic reactions that result in the synthesis of larger more complex molecules. The processes of making and breaking down sugar molecules illustrate two examples of metabolic pathways.
The two principal storage forms of energy within cells polysaccharides and lipids can also be broken down to produce ATP. Photosynthesis is an anabolic process while cellular respiration is a catabolic process. Begin typing glycolysis and then choose the pathway name from the list that.
This is the pathway which contributes to the production of food for all the animals on the earth. Aerobic and Anaerobic oxygen determines which pathway overall equation for. The photosynthesis is an anabolic process.
This pathway has other pathways within it like 1. The energy is released by the break down of the glucose. That kind of diagram is describing.
In cells this pathway occurs mainly in the mitochondria of cells. To provide gold open access this journal has a publication fee which needs to be met by the authors or their research funders for each article published open access. Glycolysis fatty acid synthesis and glycogen synthesis happen in the cytoplasm along with some steps of amino acid breakdown.
The major products of glycolysis and the TCA cycle for example are carbon dioxide and waterWithin the cell the concentrations of both are unlikely to vary sufficiently to allow them to serve as effective regulatory metabolites. A The products of one pathway are substrates for another pathway. This pathway occurs primarily in plants and few microbes.
This search is equipped with a type-ahead function for finding the metabolic pathway name. Shonnard Michigan Technological University 6 Types of Metabolism Catabolism Metabolic reactions in the cell that degrade a substrate into smaller simpler products. A covalent modification involves an addition or removal of a chemical bond whereas a non-covalent modification also known as allosteric regulation is the binding of the regulator to the enzyme via hydrogen bonds electrostatic interactions and Van Der Waals forces.
A binding of the end product of a metabolic pathway to the first enzyme in the pathway to inhibit the enzyme B one enzyme in a metabolic pathway passing its product to act as a substrate for the next enzyme in the pathway C binding a substrate to one subunit of a tetramer stimulates faster binding of substrate to each of the other three subunits. Biology questions and answers. Metabolic pathways based on the pathway name or identifier or using genes or compoundsinvolved in the pathway.
Cells have evolved to use feedback inhibition to regulate enzyme activity in metabolism by using the products of the enzymatic reactions to inhibit further enzyme activityMetabolic reactions such as anabolic and catabolic processes must proceed according to the demands of the cell. It is characteristic of catabolic routes that they do not lead to uniquely identifiable end products. Part B - Metabolic Pathways and Cellular Location Maintaining blood glucose levels is an important homeostatic activity of the body not specifically because every cell of the body must have glucose but primarily because the brain relies on glucose for its metabolism.
Chapter eight Question seven asked us to draw out a reaction pathway Im using. Oh oh conform either r or P p forms que and our forms s from there we can do our inhibition Arrows s inhibits Oh toe are que inhibits 02 p in o inhibits l to em. Nucleotides for example can be broken down to sugars which then enter the glycolytic pathway and amino acids are degraded via the citric acid cycle.

Energy And Metabolism Boundless Biology

Nutrient Metabolism Human Learn Science At Scitable

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable
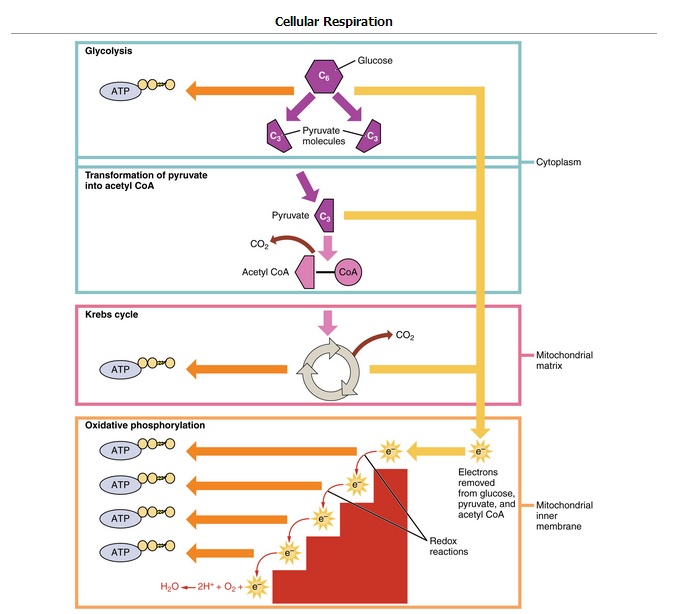
5 4a Importance Of Glycolysis Biology Libretexts

Gene Expression Regulates Cell Differentiation Learn Science At Scitable
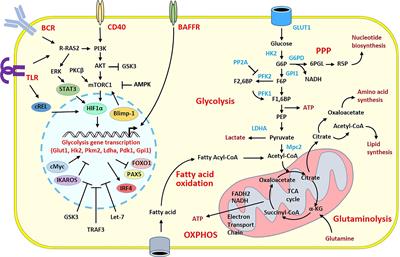
Frontiers Metabolic Program Of Regulatory B Lymphocytes And Influence In The Control Of Malignant And Autoimmune Situations Immunology

Interactive Metabolic Pathways Map

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable

Protein Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
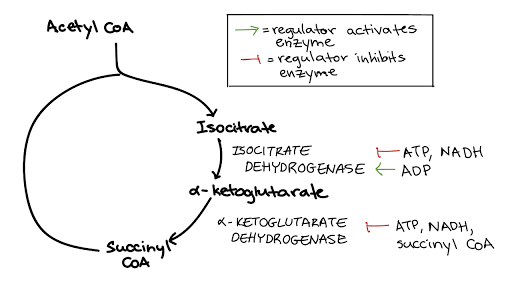
Regulation Of Cellular Respiration Article Khan Academy

Cell Metabolism Learn Science At Scitable
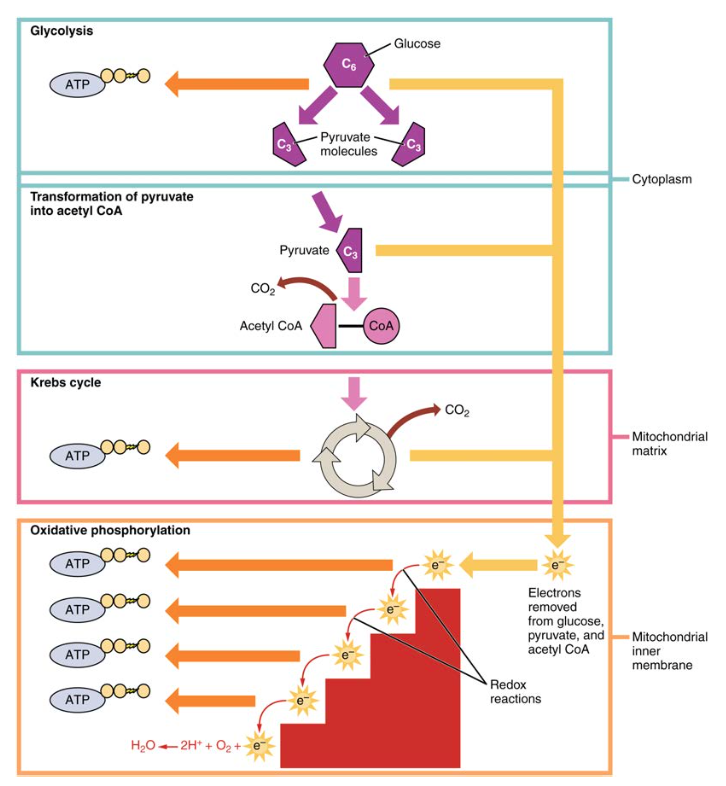
Carbohydrate Metabolism Anatomy And Physiology Ii
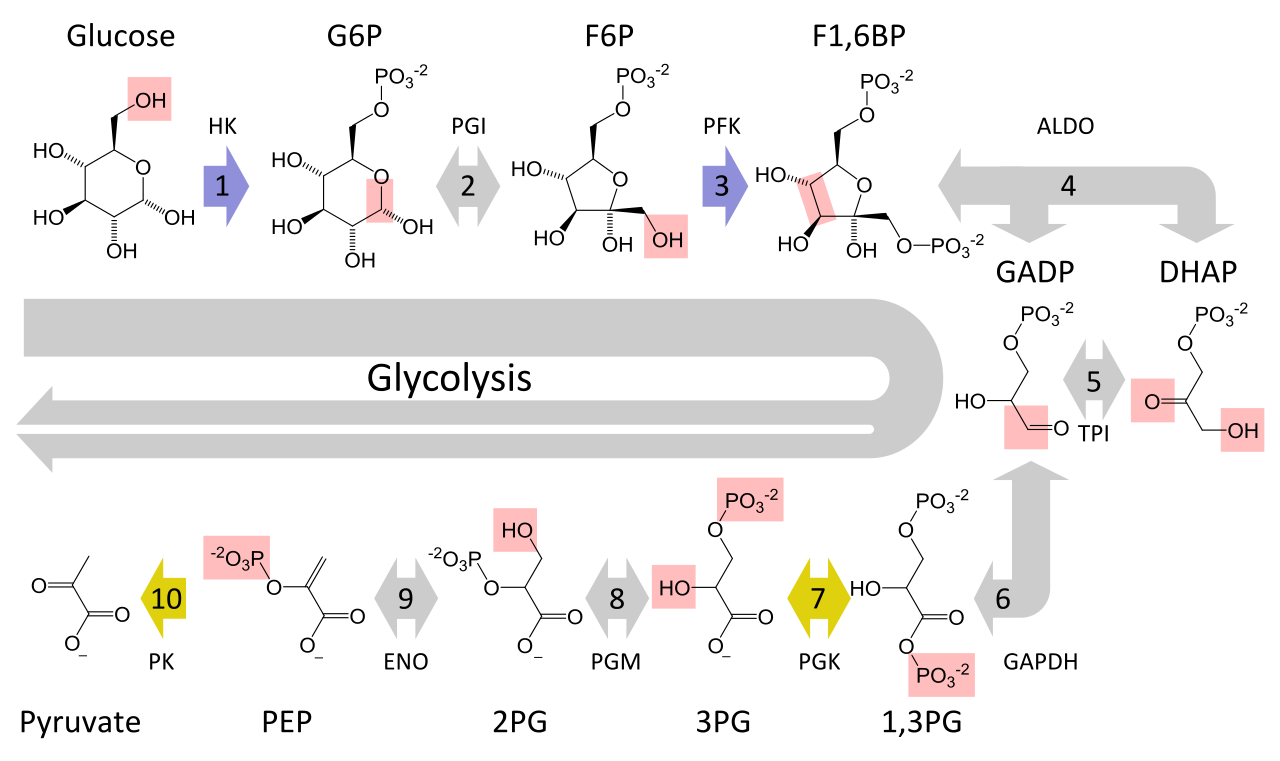
Cellular Respiration Biology For Majors I

6 2 Metabolism Overview Medicine Libretexts

Cell Metabolism Cell Biology Tocris Bioscience

Metabolic Pathways Microbiology

Metabolic Regulation Of Tissue Stem Cells Trends In Cell Biology

4 1 Metabolism Overview Medicine Libretexts
4 1 Energy And Metabolism Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Comments
Post a Comment